Table of Contents
- 2.1 General Installation Guidance
- 2.1.1 Supported Platforms
- 2.1.2 Which MySQL Version and Distribution to Install
- 2.1.3 How to Get MySQL
- 2.1.4 Verifying Package Integrity Using MD5 Checksums or GnuPG
- 2.1.5 Installation Layouts
- 2.1.6 Compiler-Specific Build Characteristics
- 2.2 Installing MySQL on Unix/Linux Using Generic Binaries
- 2.3 Installing MySQL on Microsoft Windows
- 2.3.1 MySQL Installation Layout on Microsoft Windows
- 2.3.2 Choosing an Installation Package
- 2.3.3 MySQL Installer for Windows
- 2.3.4 Installing MySQL on Microsoft Windows Using a
noinstallZIP Archive - 2.3.5 Troubleshooting a Microsoft Windows MySQL Server Installation
- 2.3.6 Windows Postinstallation Procedures
- 2.3.7 Windows Platform Restrictions
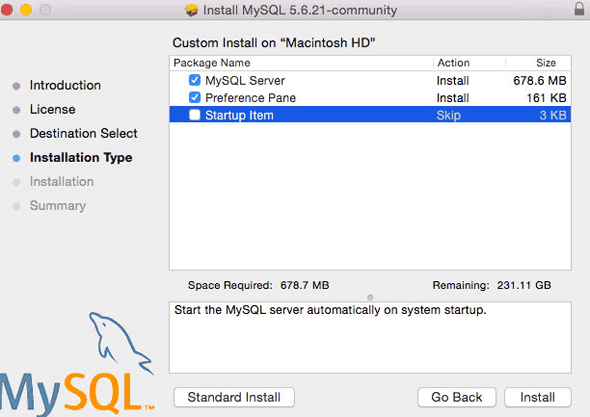
- 2.4 Installing MySQL on macOS
- 2.4.1 General Notes on Installing MySQL on macOS
- 2.4.2 Installing MySQL on macOS Using Native Packages
- 2.4.3 Installing and Using the MySQL Launch Daemon
- 2.4.4 Installing and Using the MySQL Preference Pane
- 2.5 Installing MySQL on Linux
- 2.5.1 Installing MySQL on Linux Using the MySQL Yum Repository
- 2.5.2 Installing MySQL on Linux Using the MySQL APT Repository
- 2.5.3 Installing MySQL on Linux Using the MySQL SLES Repository
- 2.5.4 Installing MySQL on Linux Using RPM Packages from Oracle
- 2.5.5 Installing MySQL on Linux Using Debian Packages from Oracle
- 2.5.6 Deploying MySQL on Linux with Docker
- 2.5.7 Installing MySQL on Linux from the Native Software Repositories
- 2.5.8 Installing MySQL on Linux with Juju
- 2.5.9 Managing MySQL Server with systemd
- 2.6 Installing MySQL Using Unbreakable Linux Network (ULN)
- 2.7 Installing MySQL on Solaris
- 2.7.1 Installing MySQL on Solaris Using a Solaris PKG
- 2.8 Installing MySQL on FreeBSD
- 2.9 Installing MySQL from Source
- 2.9.1 Source Installation Methods
- 2.9.2 Source Installation Prerequisites
- 2.9.3 MySQL Layout for Source Installation
- 2.9.4 Installing MySQL Using a Standard Source Distribution
- 2.9.5 Installing MySQL Using a Development Source Tree
- 2.9.6 Configuring SSL Library Support
- 2.9.7 MySQL Source-Configuration Options
- 2.9.8 Dealing with Problems Compiling MySQL
- 2.9.9 MySQL Configuration and Third-Party Tools
- 2.9.10 Generating MySQL Doxygen Documentation Content
- 2.10 Postinstallation Setup and Testing
- 2.10.1 Initializing the Data Directory
- 2.10.2 Starting the Server
- 2.10.3 Testing the Server
- 2.10.4 Securing the Initial MySQL Account
- 2.10.5 Starting and Stopping MySQL Automatically
- 2.11 Upgrading MySQL
- 2.11.1 Before You Begin
- 2.11.2 Upgrade Paths
- 2.11.3 What the MySQL Upgrade Process Upgrades
- 2.11.4 Changes in MySQL 8.0
- 2.11.5 Preparing Your Installation for Upgrade
- 2.11.6 Upgrading MySQL Binary or Package-based Installations on Unix/Linux
- 2.11.7 Upgrading MySQL with the MySQL Yum Repository
- 2.11.8 Upgrading MySQL with the MySQL APT Repository
- 2.11.9 Upgrading MySQL with the MySQL SLES Repository
- 2.11.10 Upgrading MySQL on Windows
- 2.11.11 Upgrading a Docker Installation of MySQL
- 2.11.12 Upgrade Troubleshooting
- 2.11.13 Rebuilding or Repairing Tables or Indexes
- 2.11.14 Copying MySQL Databases to Another Machine
- 2.12 Downgrading MySQL
- 2.13 Perl Installation Notes
- 2.13.1 Installing Perl on Unix
- 2.13.2 Installing ActiveState Perl on Windows
- 2.13.3 Problems Using the Perl DBI/DBD Interface
MySQL Workbench is available for Mac OS X and is distributed as a DMG file. The file is named mysql-workbench-oss-version-osx10.5-i686.dmg, where version is the MySQL Workbench version. To install MySQL Workbench on Mac OS X, simply download the file. Double-click the downloaded file. Getting Started with MySQL Database Service (MDS) Start here if you're familiar with OCI, but new to MDS.
This chapter describes how to obtain and install MySQL. A summary of the procedure follows and later sections provide the details. If you plan to upgrade an existing version of MySQL to a newer version rather than install MySQL for the first time, see Section 2.11, “Upgrading MySQL”, for information about upgrade procedures and about issues that you should consider before upgrading.
If you are interested in migrating to MySQL from another database system, see Section A.8, “MySQL 8.0 FAQ: Migration”, which contains answers to some common questions concerning migration issues.
Installation of MySQL generally follows the steps outlined here:
Determine whether MySQL runs and is supported on your platform.
Please note that not all platforms are equally suitable for running MySQL, and that not all platforms on which MySQL is known to run are officially supported by Oracle Corporation. For information about those platforms that are officially supported, see https://www.mysql.com/support/supportedplatforms/database.html on the MySQL website.
Choose which distribution to install.
Several versions of MySQL are available, and most are available in several distribution formats. You can choose from pre-packaged distributions containing binary (precompiled) programs or source code. When in doubt, use a binary distribution. Oracle also provides access to the MySQL source code for those who want to see recent developments and test new code. To determine which version and type of distribution you should use, see Section 2.1.2, “Which MySQL Version and Distribution to Install”.
Download the distribution that you want to install.
For instructions, see Section 2.1.3, “How to Get MySQL”. To verify the integrity of the distribution, use the instructions in Section 2.1.4, “Verifying Package Integrity Using MD5 Checksums or GnuPG”.
Install the distribution.
To install MySQL from a binary distribution, use the instructions in Section 2.2, “Installing MySQL on Unix/Linux Using Generic Binaries”. Alternatively, use the Secure Deployment Guide, which provides procedures for deploying a generic binary distribution of MySQL Enterprise Edition Server with features for managing the security of your MySQL installation.
To install MySQL from a source distribution or from the current development source tree, use the instructions in Section 2.9, “Installing MySQL from Source”.
Perform any necessary postinstallation setup.
After installing MySQL, see Section 2.10, “Postinstallation Setup and Testing” for information about making sure the MySQL server is working properly. Also refer to the information provided in Section 2.10.4, “Securing the Initial MySQL Account”. This section describes how to secure the initial MySQL
rootuser account, which has no password until you assign one. The section applies whether you install MySQL using a binary or source distribution.If you want to run the MySQL benchmark scripts, Perl support for MySQL must be available. See Section 2.13, “Perl Installation Notes”.
Instructions for installing MySQL on different platforms and environments is available on a platform by platform basis:
Unix, Linux, FreeBSD
For instructions on installing MySQL on most Linux and Unix platforms using a generic binary (for example, a
.tar.gzpackage), see Section 2.2, “Installing MySQL on Unix/Linux Using Generic Binaries”.For information on building MySQL entirely from the source code distributions or the source code repositories, see Section 2.9, “Installing MySQL from Source”
For specific platform help on installation, configuration, and building from source see the corresponding platform section:
Linux, including notes on distribution specific methods, see Section 2.5, “Installing MySQL on Linux”.
IBM AIX, see Section 2.7, “Installing MySQL on Solaris”.
FreeBSD, see Section 2.8, “Installing MySQL on FreeBSD”.
Microsoft Windows
For instructions on installing MySQL on Microsoft Windows, using either the MySQL Installer or Zipped binary, see Section 2.3, “Installing MySQL on Microsoft Windows”.
For details and instructions on building MySQL from source code using Microsoft Visual Studio, see Section 2.9, “Installing MySQL from Source”.
macOS
For installation on macOS, including using both the binary package and native PKG formats, see Section 2.4, “Installing MySQL on macOS”.
For information on making use of an macOS Launch Daemon to automatically start and stop MySQL, see Section 2.4.3, “Installing and Using the MySQL Launch Daemon”.
For information on the MySQL Preference Pane, see Section 2.4.4, “Installing and Using the MySQL Preference Pane”.
Chapter 3. Installing and Launching MySQL Workbench
Table of Contents
- 3.1. Hardware Requirements
- 3.2. Software Requirements
- 3.3. Starting MySQL Workbench
- 3.3.1. Installing MySQL Workbench on Windows
- 3.3.2. Launching MySQL Workbench on Windows
- 3.3.3. Uninstalling MySQL Workbench on Windows
- 3.3.4. Installing MySQL Workbench on Linux
- 3.3.5. Launching MySQL Workbench on Linux
- 3.3.6. Uninstalling MySQL Workbench on Linux
- 3.3.7. Installing MySQL Workbench on Mac OS X
- 3.3.8. Launching MySQL Workbench on Mac OS X
- 3.3.9. Uninstalling MySQL Workbench on Mac OS X
- 3.4. Activation Procedure (Commercial Version)
MySQL Workbench is available for the following platforms:
Binary distributions of MySQL Workbench are avaliable for the above platforms. Source code distributions are also available as a tar.gz package, or an RPM package.
The following sections explain the installation process for each of these platforms.
MySQL Workbench requires a current system to run smoothly. The minimum hardware requirements are:
CPU: Intel Core or Xeon 3GHz (or Dual Core 2GHz) or equal AMD CPU
Cores: Single (Dual/Quad Core is recommended)
RAM: 4 GB (6 GB recommended)
Graphic Accelerators: nVidia or ATI with support of OpenGL 1.5 or higher
Display Resolution: 1280×1024 is recommended, 1024×768 is minimum.
Mysql Data Location Mac
The following operating systems are officially supported:
Windows 7 (64-bit, Professional level or higher)
Mac OS X 10.6.1+
Ubuntu 9.10 (64bit)
Ubuntu 8.04 (32bit/64bit)
For convenience the following builds are also available:
Windows XP SP3, Vista
Mac OSX (10.5 and 10.6) Intel
Ubuntu 8.04 (i386/x64)
Ubuntu 9.04 (i386/x64)
Fedora 11 (i386/x64)
MySQL Workbench also has the following general requirements:
The Microsoft .NET 3.5 Framework.
Cairo 1.6.0 or later
glib-2.10
libxml-2.6
libsigc++ 2.0
pcre
libzip
For convenience the Windows libraries are available as the download “Dependencies for Compiling in Windows”.
On start up, the application checks the OpenGL version and selects between software and hardware rendering. To determine the rendering method that is being used, open the Help menu and choose the System Info submenu.
- 3.3.1. Installing MySQL Workbench on Windows
- 3.3.2. Launching MySQL Workbench on Windows
- 3.3.3. Uninstalling MySQL Workbench on Windows
- 3.3.4. Installing MySQL Workbench on Linux
- 3.3.5. Launching MySQL Workbench on Linux
- 3.3.6. Uninstalling MySQL Workbench on Linux
- 3.3.7. Installing MySQL Workbench on Mac OS X
- 3.3.8. Launching MySQL Workbench on Mac OS X
- 3.3.9. Uninstalling MySQL Workbench on Mac OS X
The procedure for launching MySQL Workbench depends on the platform. Generally, there are two ways to launch MySQL Workbench from the command line and from the graphical user interface of the host operating system. Using the command-line launching facility is useful when you want to customize some aspects of the way MySQL Workbench operates. Launching MySQL Workbench for each of the supported platforms is described in the following sections.
In addition to platform-specific command line options, MySQL Workbench has the following command line options:
--admin- Launch MySQL Workbench and load the server instance specified.instance--query- Launch MySQL Workbench and load the connection specified.connection--model- Launch MySQL Workbench and load the model specified.modelfile--script- Launch MySQL Workbench and run the script specified.script--run- Launch MySQL Workbench and run the code snippet specified.code--quit-when-done- quits MySQL Workbench after --script or --run finishes.
MySQL Workbench may be installed using the Windows installer file or it may be installed manually from a ZIP file.
Installing MySQL Workbench Using the Installer
MySQL Workbench can be installed using the Windows Installer (.msi) installation package. The MSI package bears the name mysql-workbench-, where version-win32.msiversion indicates the MySQL Workbench version number.
Installing MySQL Workbench using the installer requires either Administrator or Power User privileges. If you are using the ZIP file without an installer, you do not need Administrator or Power User privileges.
Improving the MySQL Installation Wizard depends on the support and feedback of users. If you find that the MySQL Installation Wizard is lacking some feature important to you, or if you discover a bug, please report it in our bugs database. To do this use the Report a Bug option under the Help menu.
To install MySQL Workbench, right-click the MSI file and select the Install option from the pop-up menu, or simply double-click the file.
In the Setup Type window you may choose a
CompleteorCustominstallation. To use all features of MySQL Workbench choose theCompleteoption.Unless you choose otherwise, MySQL Workbench is installed in
C:, where%PROGRAMFILES%MySQLMySQL Workbench 5.1edition_type%PROGRAMFILES%is the default directory for programs for your locale. The%PROGRAMFILES%directory may beC:Program FilesorC:programme.
Installing from the ZIP File
If you are having problems running the installer, as an alternative, you can download a ZIP file without an installer. That file is called mysql-workbench-. Using a ZIP utility, unpack it to the directory of your choice. You may also want to create a shortcut on your desktop or the quick launch bar. version-win32.zip
To install using the ZIP file, download the ZIP file to a convenient location and decompress the file. You can place the resulting directory anywhere on you system. You do not need to install or configure the application before using it.
To start MySQL Workbench on Windows select Start, Programs, MySQL and then select MySQL Workbench.
You may also start MySQL Workbench from the command line. To view the available command-line options, issue the command MySQLWorkbench -help | more from the MySQL Workbench installation directory. You will see the following output:
The MySQL Workbench version number is displayed followed by a usage message and then the options. Use the -swrendering option if your video card does not support OpenGL 1.5. The -version option can be used to display the MySQL Workbench version number. The -grtversion can be used to display the GRT shell version number. The other options are self-explanatory.
When using command-line options that display output to a console window, namely -help and -version, be sure that you pipe the output through the more command otherwise nothing will be displayed.
The method for uninstalling MySQL Workbench will depend on how you install MySQL Workbench in the first place.
Rmoving MySQL Workbench when installed Using the Installer
To uninstall MySQL Workbench, open the Control Panel and Choose Add or Remove Programs. Find the MySQL Workbench entry and choose the button. Doing this will remove MySQL Workbench.
Any modules added to the
C:Program FilesMySQLMySQL Workbenchdirectory will not be deleted.versionmodules
It is not possible to remove MySQL Workbench from the command line if you have installed MySQL Workbench using the installer. Although you can manually remove some of the compoentns There is no command-line option for removing MySQL Workbench.
Removing the MySQL Workbench directory manually will not remove all the files belonging to MySQL Workbench.
When installed from a ZIP file
If you installed MySQL Workbench using a ZIP file, to remove MySQL Workbench you can just delete the MySQL Workbench directory.
If you installed any additional modules within the modules directory and you want to keep them, make sure you copy those modules to a different directory before deleting the MySQL Workbench directory.
There are several binary distributions of MySQL Workbench available for Linux. These include:
Fedora 10 amd64 (RPM)
Ubuntu 8.04 i386 (DEB)
Ubuntu 8.10 amd64 (DEB)
In addition to the binary distributions, it is also possible to download the MySQL Workbench source code as a tar.gz or RPM package.
Check the MySQL Workbench download page for the latest packages.
The procedure for installing on Linux depends on which Linux distribution you are using.
Installing DEB packages
On Ubuntu, and other systems that use the Debian package scheme, you can install MySQL Workbench using a command such as:
Note that package.debmysql-workbench-oss-, where version_i386.debversion is the MySQL Workbench version number.
You may be warned that certain libraries are not available, depending on what you already have installed. Install the required libraries and then install the MySQL Workbench package again.
Installing RPM packages
On RedHat-based systems, and other systems using the RPM package format, MySQL Workbench can be installed by a command such as:

Again, note that package.rpmmysql-workbench-oss-, and version-1fc10.x86_64.rpmversion is the MySQL Workbench version number.

Once MySQL Workbench has been installed it can be launched by selecting Applications, Programming, MySQL Workbench from the main menu.
MySQL Workbench can also be launched from the command line on Linux. Type the command:
This will display the available command-line options:
The procedure for uninstalling MySQL Workbench on Linux depends on the packe you are using.
Uninstalling DEB packages
For Debian packages the command is:
This does not remove the configuration files. If you wish to also remove the configuration files use:
Uninstalling RPM packages
To uninstall RPM packages use:
This does not remove the configuration files.
MySQL Workbench is available for Mac OS X and is distributed as a DMG file. The file is named mysql-workbench-oss-, where version-osx10.5-i686.dmgversion is the MySQL Workbench version.
To install MySQL Workbench on Mac OS X, simply download the file. Double-click the downloaded file. You will be presented with the installation screen:
Figure 3.1. MySQL Workbench Mac OS X Installation Screen
Drag the MySQL Workbench icon onto the Application icon as instructed. MySQL Workbench is now installed.
You can now launch MySQL Workbench from the Applications folder.
To launch MySQL Workbench on Mac OS X, simply open the Applications folder in the Finder, then double-click MySQL Workbench.
Mysql Database Location Mac
It is also possible to start MySQL Workbench from the command line:
A model file must be specified.
Mysql Directory Mac
To uninstall MySQL Workbench for Mac OS X, simply locate MySQL Workbench in the Applications folder, right-click, and select Move to Trash. The application is uninstalled.
